Do while loop in C
Learn via video course

Overview
A loop is a method to repeat a set of instructions or code-block until a condition remains true. We use a loop to get rid of writing the same statements again and again.
do..while() is a loop in which a set of instructions will execute at least once (irrespective of the condition) and then the repetition of loop's body will depend on the condition passed at the end of the loop in the while() function. It is also known as an exit-controlled loop.
Scope
- This article explains do-while loop in c.
- This article contains various examples of do while loop and a comparison with the while loop.
Syntax of Do While loop in C
Syntax for do...while() loop in C is as follows:
Explanation of terminologies used:
-
initialization : Generally we use an iterator variable (like int i = 0;) in the initialization statement to use this variable in the update expression and in the exit condition of the loop.
-
instruction(s) : It has some set of statements that we want to repeat and an update expression, these are known as the body of the loop.
-
update expression : In general, it is some increment/decrement statement of initialized variable related to the condition at the bottom of the loop.
-
condition : A boolean expression (either true or false) passed at the bottom of the loop to determine if the loop should repeat itself or not.
Note : There should always be a semi-colon ; at the end of a do...while() loop, otherwise the compiler will give a syntax error.
Flow Diagram of Do While loop in C
Let us see the flow of do...while() loop through a diagram to understand it better.

Example
Below is the code to print integers between 0 and 10 using a do...while() loop.
Output:
Explanation:
- In the first statement of the main() function, we have declared and initialized an integer variable i = 1.
- In the body of do-while() loop, we have a printf("%d ", i); statement i.e. used to print the integer values in the output.
- In the first iteration, the value of i = 1 so it prints 1 in the output.
- We have an update expression i++; i.e. used to increase the value of i = i + 1;.
- Further iterations will print the successive value of i in the output i.e. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9.
- When i becomes 10, the condition in the while() holds false, so the control from the loop exits and shifts to the next statement i.e. return 0; and the program ends.
Flow chart for the above code:
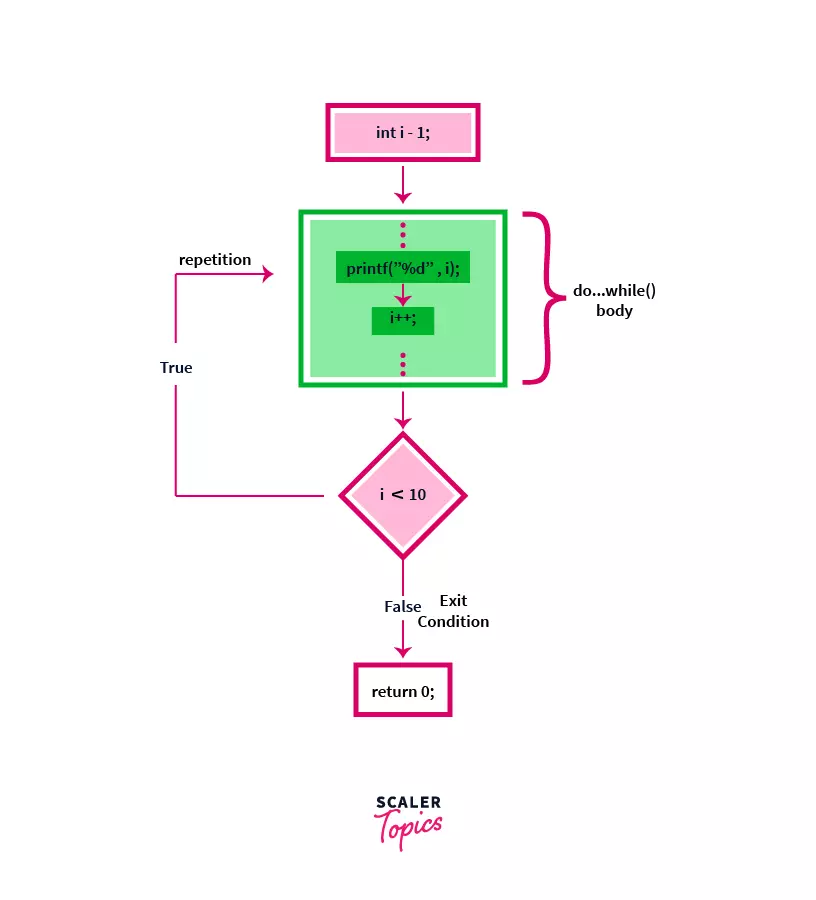
How Do-While loop works in C?
In a do-while loop, we are entering the body of the loop without checking any condition, so in this loop, the code in the body of the loop will execute at least once and then a boolean condition (either true or false) is checked that is passed as an argument in the while() function at the bottom of the loop. If the condition holds true, the control will again shift to the statements inside of the loop body and this process will repeat itself until the condition becomes false. This property of exit-control in do...while() loop makes it different from the other two loops available in the C Language, i.e. for-loop and while-loop that checks the condition at the beginning of the loop and are known as entry controlled loops.
Flow explanation of do...while() loop
- First, there is an initialization statement before entering into the body of the loop. Example, int i = 0;
- Now, control will directly go inside the do...while() block and instructions will be executed at least once, irrespective of the condition at the bottom. Example, printf("%d", i);
- An update expression is used to update the initialized variable and to fulfill the exit condition (otherwise it will be an infinite loop). Example, i++;
- If the condition is true it will repeat the execution of the statements inside the block, else control will exit from the do...while() loop will shift to the next statement. Example condition, while(i < 10);
Examples of Do While loop in C
Let us look at a real-world example of do...while() loop and then we will look at some coding examples of do...while() loop.
Let's suppose, you have set an alarm clock to buzz at 05:00AM in the morning (body of the loop). It will go off at 05:00AM in the morning i.e. at least once, and suppose the condition at the end of the loop is that if you have snoozed your alarm or not. If you have snoozed (i.e. true), it will buzz again after a certain time and it will not buzz if you have set the alarm off without snoozing it (i.e. false).
Now, let us look at some of the do...while() loop code examples.
In the first example, we are writing a program for finding the average of first N natural numbers using a do...while() loop in C.
Code:
Input
Enter the value of N : 12
Output :
Sum : 78
Average of 12 numbers : 6.50
Explanation :
- Two integer variable sum = 0 and i = 0 are declared and initialized in the main() function. These are known as the initialization statements.
- An integer variable N and a float variable avg are also declared but not initialized.
- In the above example, we have taken 12 as an input number to store in N using the scanf() statement.
- Now, the body of do...while() loop starts. Control directly shifts inside the do block and statements start executing.
- We have an instruction sum += i, which updates the value of sum to the addition of sum and i variables in every iteration.
- i++; is an update expression i.e. used to fulfill the below condition and exit the loop at a certain point.
- while( i <= N); checks the condition and repeat the loop if it holds true, and exits if false.
- In the above example, the loop exits when i = 13 i.e. i is not less than N anymore. The control will shift to the next statements outside the loop.
- We now calculate the avg using the sum and N values.
- Formula : Average = Sum of N Numbers / N.
- Now, the average of N numbers is printed using the avg variable and the printf() statement.
In this example, we are going to print a multiplication table of an input number N.
Code:
Input
Output :
Explanation:
- First, an integer variable i is declared and initialized with 1 in the main() function. It is known as the initialization statement.
- A variable N is also declared but not initialized. N has been taken as input from the user.
- Now, the body of do...while() loop starts. Control directly shifts inside the do block and statements start executing.
- printf("%d * %d = %d\n", N, i, N * i); statement is used to print the multiplication table of N. In the above example, we have taken N to be 5.
- i will go from 1 to 10 using the update expression i++;. At each iteration/repetition the print statement will be executed with an increased i value.
- At i = 11, the condition will hold false, so the control will exit from the loop and shift to the next statement after the loop.
while() vs do...while() loop in C
Let us look at the differences of while() and do...while() loop, then we will see an example to understand the differences better.
| while() loop | do...while() loop |
|---|---|
| It is known as an entry-controlled loop. | It is known as an exit-controlled loop. |
| In a while() loop, first we check the boolean expression, if it holds true, the control will go inside the loop, and execution of the statements will take place and repeat until the expression becomes false, else if in the beginning the expression is false the control will not go inside the body and loop ends. | In a do...while() loop, we are entering the body of the loop without checking any condition, so in this case, the code inside the body of loop will execute at least once. Then, a condition is checked, if it is true then again body of loop is executed otherwise loop ends, and control shifts to the next statement. |
| In this loop, we use a while keyword. | In this loop, we use a do-while keyword. |
Let us try to print "Scaler Topics - Do While Loop in C" string using both while and do...while() loops.
do...while() loop
Code:
Output :
while() loop
Code:
Output :
Difference
- do...while() loop executes at least once, even if the condition passed is false. Therefore, it prints the strings Scaler Topics - Do While Loop in C and Out of loop in the output.
- while() loop doesn't execute as it is an entry-controlled loop and checks the condition before entering into the loop. Therefore, it doesn't print Scaler Topics - Do While Loop in C in the output and directly prints Out of loop.
Conclusion
- We have learned about the do-while loop in C Language.
- In a do-while loop, the statements inside the loop will execute at least once irrespective of the condition at the bottom of the loop and it is also known as is an exit-controlled loop.
- We also learned about the differences between while and do-while loop.
